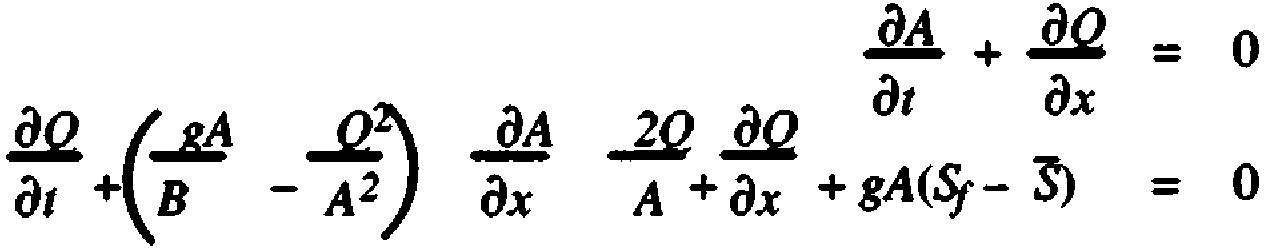|
California Code of Regulations (Last Updated: August 6, 2014) |
 |
Title 19. Public Safety |
 |
Division 2. California Emergency Management Agency |
 |
Chapter 2. Emergencies and Major Disasters |
 |
Subchapter 4. Dam Inundation Mapping Procedures |
§ 2575.2. Definitions.
Latest version.
- For purposes of this Subchapter only, the terms listed below shall have the meanings noted:(a) “Agency”: The Governor's California Emergency Management Agency.(b) “Alteration”: Has the same meaning as specified in Section 6006 of the Water Code.(c) “Appropriate Public Safety Agency”: Any city, city and county, county, state, or other public agency organized, existing, and acting pursuant to the law, which is authorized under the law to exercise police power to establish emergency procedures and effect emergency actions within its jurisdiction.(d) “Breach”: A sudden opening through a dam that drains the reservoir. An uncontrolled breach is one that results in an unintentional discharge from the reservoir.(e) “Breach elevation”: The elevation of the water in a reservoir above sea level at the time of the dam failure using the National Geodetic Vertical Datum of 1929 (NGVD) standard (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, National Geodetic Survey).(f) “Breach time”: The modeled time elapsed from initial dam failure to total dam failure.(g) “Cross-section”: A lower elevation point or linear representation on an inundation map where flood measurements are calculated.(h) “Dam”: Has the same meaning as specified in Sections 6002, 6003, and 6004 of the Water Code.(i) “Dam Owner”: The person, agency, jurisdiction or other legal entity responsible for a dam.(j) “Debris”: Soil, rock, and organic matter carried by the floodwaters that emanate from a watershed.(k) “Debris Basin”: A permanent flood control facility that has the primary purpose of separating debris from the floodwaters and storing the debris for future removal.(l) “Debris Dam”: A dam that has the primary purpose of holding back debris captured in, and stored by the debris basin.(m) “Deflood time”: The time elapsed from the initial failure of the dam until the measured location returns to its preflood water elevation prior to the failure.(n) “Design Flood”: The flood magnitude that a dam will be subject to for analysis in a dam failure study. When a federal survey has been authorized, the design probable maximum flood will be determined by the appropriate federal agency.(o) “Dynamic Routing”: Hydraulic flow routing based on the solution of the St.-Venant equation(s) to compute the changes of discharge and stage with respect to time at various locations along a stream. St.-Venant equations are nonlinear hyperbolic partial differential equations. The equations are derived from mass and momentum balances and are given bywhere A is the cross sectional area of the channel, B is the width of the water surface, Q is the flow (discharge), g is the gravity, Sf is the friction slope, and S is the mean bed slope. The friction slope is a nonlinear function of the channel geometry. In the above equation it is assumed that the lateral inflow is zero.(p) “Enlargement”: Has the same meaning as specified in Section 6007 of the Water Code.(q) “Flood”: A temporary rise in water surface elevation of one foot or more greater than that existing under pre-dam failure conditions resulting in inundation of areas not normally covered by water as a result of a dam failure.(r) “Flood Routing”: A process of determining progressively the amplitude of a flood wave as it moves past a dam and continues downstream.(s) “Flood Stage”: A flood height at which a watercourse overtops its banks and begins to cause damage to any portion of the defined reach.(t) “Flood Storage”: The retention of water or delay of runoff either by planned operation, as in a reservoir, or by temporary filling of overflow areas, as in the progression of a flood wave through a natural stream channel.(u) “Floodwave arrival time”: The time counted from the failure of the dam until the arrival of the wave front (or leading edge of the flood wave). A flood wave is a minimum of one (1) foot increase in the level of water above the stream flow or natural surface elevation before the dam failure.(v) “Floodwave maximum elevation”: This is the highest flood stage elevation of the floodwaters as it passes a specific location. Floodwave maximum elevation cannot be less than the normal water elevation prior to the dam failure event because a “no flooding” condition exists.(w) “Freeboard”: Vertical distance between a specified stillwater reservoir surface elevation and the top of the dam, without camber.(x) “Full”: For an on stream dam, the maximum elevation of the water in the reservoir during the Inflow Design Flood (IDF); for an off stream dam, the maximum elevation of the water in the reservoir at the dam crest.(y) “Hydrograph”: A graphical representation of the water discharge with respect to time for a particular point on a stream, river or at the point of breach.(z) “Inflow Design Flood (IDF)”: The flood flow above which the incremental increase in downstream water surface elevation due to failure of a dam or other water impounding structure is no longer considered to present an unacceptable additional downstream threat. The upper limit of the IDF is the probable maximum flood.(aa) “Inundation Area”: The area downstream of a dam that would be inundated or otherwise affected by the failure of the dam and accompanying large flood flows.(bb) “Inundation Map”: A map, as specified in Government Code 8589.5, showing the area that would be inundated by flooding from an uncontrolled release of a dam's reservoir.(cc) “Inundation Pathway”: The boundary of the floodwaters released by a dam failure.(dd) “Overtopping”: The mode of dam failure wherein reservoir waters exceed crest elevation and the resultant flow causes failure by dam crest erosion.(ee) “Peak flow”: The water flow expressed in cubic feet per second (cfs) at the floodwave maximum elevation.(ff) “Probable Maximum Flood (PMF)”: The flood that may be expected from the most severe combination of critical meteorological and hydrologic conditions that is reasonably possible in the drainage basin under study.(gg) “Probable Maximum Precipitation (PMP)”: Theoretically, the greatest depth of precipitation for a given duration that is physically possible over a given size storm area at a particular geographical location during a certain time of the year.(hh) “Qmax”: Maximum breach discharge as measured in cubic feet per second (cfs).(ii) “Reservoir”: Has the same meaning as specified in Section 6004.5 of the Water Code.(jj) “Reservoir Rim”: The boundary of the reservoir including all areas along the valley sides above and below the water surface elevation associated with the routing of the IDF.(kk) “Reservoir storage elevation curve”: A reservoir capacity graph representing the elevation above mean sea level and acre feet of water.(ll) “Retention Basin”: A reservoir of variable water storage capacity created by a dam designed to continuously pass flood waters in a controlled manner.(mm) “Sensitivity Analysis”: An analysis in which the relative importance of one or more of the variables thought to have an influence on the phenomenon under consideration is determined.(nn) “Stillwater Elevation”: The maximum elevation that a water surface would assume if all wave actions were absent and there were no outflows from nor inflows into the reservoir.(oo) “Surcharge”: The volume or space in a reservoir between the controlled water retention level and the maximum water level. Flood surcharge cannot be retained in the reservoir but will flow out of the reservoir until the controlled retention water level is reached.(pp) “Toe of the Dam”: The junction of the downstream slope or face of a dam with the ground surface; also referred to as the downstream toe. The junction of the upstream slope with the ground surface is called the heel or the upstream toe.(qq) “U.S.G.S. Quad”: A topographical map produced by the United States Geological Survey with a minimum scale of 1:24,000 feet for a specific geographical area.(rr) “Water storage elevation”: Has the same meaning as specified in Section 6008 of the Water Code.HISTORY1. New section filed 4-2-2002 as an emergency; operative 4-2-2002 (Register 2002, No. 14). A Certificate of Compliance must be transmitted to OAL by 7-31-2002 or emergency language will be repealed by operation of law on the following day.2. Certificate of Compliance as to 4-2-2002 order transmitted to OAL 7-31-2002; disapproved by OAL and order of repeal filed 9-12-2002 (Register 2002, No. 37).3. New section filed 9-12-2002 as an emergency; operative 9-12-2002 (Register 2002, No. 37). A Certificate of Compliance must be transmitted to OAL by 1-10-2003 or emergency language will be repealed by operation of law on the following day.4. Certificate of Compliance as to 9-12-2002 order transmitted to OAL 1-7-2003 and filed 2-4-2003 (Register 2003, No. 6).5. Change without regulatory effect adopting new subsection (a), repealing subsection (cc), relettering subsections and amending Note filed 5-12-2010 pursuant to section 100, title 1, California Code of Regulations (Register 2010, No. 20).
Note
Note: Authority cited: Sections 8567, 8585 and 8586, Government Code. Reference: Sections 8585 and 8589.5, Government Code; and Sections 6002, 6003, 6004 and 6025, Water Code.